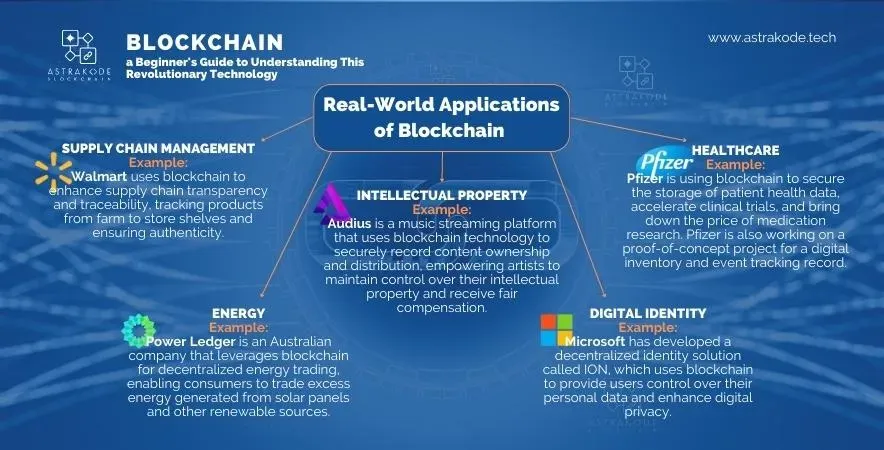
Across industries, blockchain real-world applications are redefining how organizations manage data, coordinate across partners, and unlock new business models. From enterprise blockchain solutions to real-time provenance, these uses bring trust, transparency, and efficiency to complex ecosystems. In practice, we see blockchain in supply chain improving traceability and authenticity of goods across suppliers. Data integrity with blockchain is enhanced by tamper-evident ledgers that support auditable histories. As companies scale, blockchain technology in industry and smart contracts and digital identity give shape to secure, automated workflows.
Viewed through this lens, distributed ledger technology powers practical deployments that improve transparency, traceability, and trust in supply chains, hospitals, and government services. LSI-friendly terms such as digital ledger ecosystems, permissioned networks, and interoperable data models help explain why organizations migrate from legacy systems. The focus is on governance, privacy, and performance, not speculation, with outcomes such as faster settlements, reduced reconciliation, and auditable trails. Automation is enabled by programmable rules, smart contracts, and identity primitives that preserve control over sensitive information. As industries accelerate adoption, these approaches form the backbone of reliable, scalable platforms for collaboration across ecosystems.
Blockchain Real-World Applications: Transforming Industry Through Trusted Data and Proven Use Cases
Blockchain real-world applications extend far beyond cryptocurrencies. By building trusted data networks and shared ledgers, organizations can accelerate collaboration, reduce reconciliation costs, and gain real-time visibility across complex ecosystems. In practice, enterprise blockchain solutions enable the blockchain in supply chain to provide immutable provenance, verifiable certifications, and synchronized data among suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers.
Data integrity with blockchain is a central driver for industries such as healthcare, finance, and government services. A single source of truth helps harmonize records, enables secure data sharing with privacy protections, and improves interoperability between legacy systems without exposing sensitive information.
Smart contracts and digital identity are powering automated workflows—from automated payments on delivery to tokenized assets and verifiable participant identities. Strong governance, robust cryptography, and scalable network architectures are essential to ensure that permissioned networks deliver auditable, compliant outcomes while maintaining privacy.
Implementing Enterprise Blockchain Solutions: Best Practices for Adoption, Privacy, and Interoperability
To realize blockchain real-world applications in practice, organizations must start with a clear problem statement, defined value, and a choice of architecture—public, private, consortium, or hybrid—that fits regulatory and interoperability requirements. Emphasizing enterprise blockchain solutions helps align stakeholders, governance, and technical design from the outset.
Privacy and security cannot be afterthoughts. Techniques such as data hashing, zero-knowledge proofs, and private channels help protect sensitive information while preserving the immutability and auditability of the ledger. Coupled with identity management and smart contracts, these controls enable trusted collaboration across partners in the ecosystem.
Implementation steps should include mapping data flows, defining governance, building a minimal viable product, and integrating with existing ERP/CRM systems. Start with a focused pilot, measure outcomes, and plan scale to achieve broader interoperability across the value chain and related use cases within enterprise blockchain solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do blockchain real-world applications improve supply chain transparency and data integrity with blockchain?
Blockchain real-world applications in the supply chain (blockchain in supply chain) use a shared, tamper-evident ledger to record the journey of goods from sourcing to delivery, enabling immutable provenance and real-time visibility. Enterprise blockchain solutions on permissioned networks provide auditability while preserving data privacy across partners. Smart contracts automate events like payments and recalls, and digital identity enables verifiable credentials for suppliers and customers, reducing fraud and strengthening data integrity with blockchain.
What adoption considerations should organizations weigh when pursuing enterprise blockchain solutions across industries?
Start with a clear business problem and measurable value, then choose an architecture (public, permissioned, consortium, or hybrid) that fits governance, security, and interoperability needs. In blockchain technology in industry, governance and data interoperability are critical to avoid silos, and privacy controls (private channels, hashing, or zero-knowledge proofs) are essential for sensitive data. Plan for data model design, integration with existing systems, pilot-to-scale strategies, and ongoing regulatory alignment to ensure scalable and compliant outcomes.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Overview | Blockchain is a distributed, tamper‑evident ledger that enables trust and collaboration beyond digital currencies; it supports data integrity, governance, and operational efficiency. |
| Supply Chain | Tracks origin and milestones, provides an immutable audit trail, enhances traceability, reduces fraud, and enables real‑time coordination among stakeholders. |
| Data Integrity & Interoperability | Creates a single source of truth, improves data quality, and enables secure data sharing while harmonizing records across legacy systems. |
| Finance & Enterprise Blockchain | Streamlines settlements, cross‑border payments, KYC workflows, asset tokenization, and identity management on permissioned networks. |
| Public Sector & Governance | Enhances transparency with auditable workflows in land registries, case tracking, and grant management while preserving data privacy. |
| IoT & Traceability | Secures device data, enables smart contracts, and improves maintenance and compliance across multiple organizations and devices. |
| Smart Contracts & Identity | Automates rules and payments; emphasizes privacy controls and verifiable digital identities for secure onboarding. |
| Adoption & Implementation | Defines goals, selects architecture, establishes governance, ensures privacy, piloting with measurable value, and plans for scale. |
| Challenges & Future Outlook | Addresses scalability, regulatory alignment, interoperability, and change management; expects broader adoption and integration with AI, analytics, and identity management. |
Summary
Blockchain real-world applications are moving beyond hype to deliver tangible value by improving trust, transparency, and efficiency across supply chains, finance, healthcare, and public services.