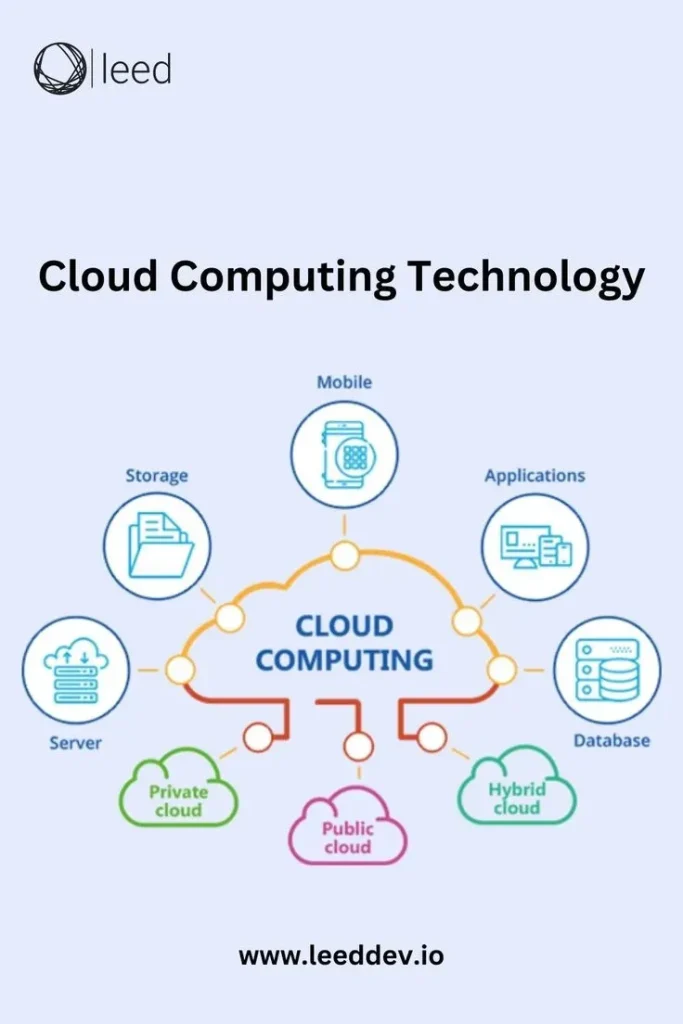
Cloud computing demystified is a practical, hands-on guide to understanding how remote servers and services delivered over the internet power modern workloads. From core concepts to real-world steps, this primer translates jargon into actionable insights you can apply today; it bridges theory and practice with practical examples, checklists, and quick experiments that don’t require heavy setup. By starting with cloud computing basics, you’ll grasp elasticity, pay-as-you-go economics, and the idea of on-demand resources. We’ll explore cloud deployment models and how to choose between public vs private cloud setups to fit your needs; we’ll also touch on hybrid approaches and what tradeoffs commonly appear in real organizations. Whether you are a student, a professional expanding your skills, or a business owner evaluating options, this guide moves you from curiosity to capability, showing why cloud services explained in plain terms matter and highlighting cloud security fundamentals, and this context helps you benchmark progress over time.
To frame this topic in other terms, think of online infrastructure you can rent or release on demand, powered by shared pools of computing power and storage. This way of talking emphasizes scalable, distributed resources rather than fixed hardware, enabling rapid experimentation and global reach. When you hear about deployment options, consider off-premise platforms, remote data centers, and service-oriented offerings that replace traditional server rooms. By focusing on ideas like elasticity, managed services, security controls, and governance, you can map needs to practical solutions without getting lost in buzzwords.
Cloud computing demystified: A practical guide to cloud computing basics and deployment models
Cloud computing basics become tangible when you see resources like virtual machines, databases, and storage delivered over the internet instead of being bought and run on premises. This model, often described as cloud services explained, unlocks on-demand capacity, global reach, and a pay-as-you-go cost structure that makes experimentation and scaling practical. By keeping the focus on cloud computing basics, readers gain a clear view of how the cloud changes who provides and manages IT services, and how to evaluate solutions with a practical mindset.
Two fundamental dimensions drive effective cloud planning: cloud deployment models and cloud service models. IaaS provides raw compute and storage while you manage the software stack; PaaS offers a ready-to-use platform that handles runtime and middleware; SaaS delivers end-user applications with minimal setup. When you pair these models with deployment options like public cloud, private cloud, hybrid, and multi-cloud, you get a practical framework to map workloads, plan small projects, and scale as needs evolve. This combination also intersects with cost considerations and security planning, shaping a balanced cloud strategy.
Public vs private cloud and security fundamentals: Making informed cloud decisions
Choosing between public vs private cloud hinges on data sensitivity, regulatory requirements, latency needs, and governance preferences. The public cloud delivers scalable resources, rapid provisioning, and cost efficiency for non-sensitive workloads, while a private cloud provides greater control and customization for regulated data. In practice, many teams use a hybrid approach to balance speed with compliance, keeping sensitive functions in a private environment while leveraging the public cloud for experimentation and burst workloads.
Security is a cornerstone of cloud decision making, and cloud security fundamentals become actionable when applied through a clear shared responsibility model. Providers secure the underlying infrastructure, while customers control data, access management, encryption, and application configuration. Build defenses around identity management, encryption at rest and in transit, monitoring, and regular security assessments. By aligning these practices with chosen deployment models and governance policies, you can reduce risk, satisfy compliance, and preserve agility and cost visibility.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Cloud computing demystified and how do cloud computing basics help beginners understand the cloud?
Cloud computing demystified is a practical guide that explains how computing resources are delivered over the internet. It starts with cloud computing basics—storage, compute, databases, and managed services—and shows how to start small and scale as needed. It also covers cloud deployment models (public, private, hybrid) and how to map workloads to the right model. Finally, it explains cloud services explained as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, and reviews cloud security fundamentals to manage risk.
How do cloud deployment models influence decisions on public vs private cloud in Cloud computing demystified?
Cloud deployment models describe where and how resources are hosted. In Cloud computing demystified, public cloud offers scalable, cost-effective resources for testing and non-sensitive workloads, while private cloud provides more control and compliance for sensitive data. A hybrid approach blends both to balance speed, governance, and cost. To decide, map workloads by data sensitivity and latency, start with a small pilot, and apply cloud security fundamentals across all models.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Cloud computing demystified means using remote internet-based resources to store, manage, and process data; benefits include flexibility, faster innovation, and potential cost savings. |
| What is Cloud Computing? | Delivery of computing resources over the internet; rent storage/compute/databases as needed; enables scalability, resilience, and global reach; pay for what you use. |
| Core Value: Elasticity & Managed Services | On-demand resource provisioning; scale up/down; managed services handle backups, monitoring, security patches; faster, reliable, and consistent operations. |
| Cloud Service Models: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS | IaaS: raw resources; user manages OS/apps; provider handles hardware. PaaS: platform/runtime; user codes; provider handles scaling. SaaS: ready-to-use apps; no infra management. |
| Deployment Models: Public, Private, Hybrid | Public: provider-owned, shared; scalable and cost-effective. Private: single org, more control; compliance. Hybrid: mix for speed and control; optimize workloads. |
| Security & Shared Responsibility | Provider secures cloud infrastructure; customers secure data, access, encryption, apps, and configurations. Use IAM, encryption, backups, regular assessments. |
| Costs & ROI | Pay-as-you-go; risk of runaway costs; control via rightsizing, offlining unused resources, budgeting, alerts, and reserved instances/savings plans. |
| Migration & Adoption | Start small with measurable value; define success metrics; monitor results; scale to more critical workloads; build cross-functional teams; plan data migration and DR. |
| Real World Use Cases | E-commerce example: IaaS for app hosting, PaaS for development, SaaS for CRM; hybrid for private customer data; demonstrates models in action. |
Summary
Conclusion: Cloud computing demystified has evolved from theory into a practical, repeatable approach. By understanding core service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and deployment options (public, private, hybrid), along with the shared security model and cost considerations, you can design scalable architectures that balance control, speed, and cost. This guide emphasizes starting small, measuring outcomes, and iterating toward cloud maturity, turning curiosity into capability for individuals and organizations alike.