Cloud gaming explained has evolved from a niche curiosity into a mainstream topic that captivates gamers, developers, and hardware makers alike. With cloud processing, the game runs on powerful data centers and streams to your screen, letting even modest devices try demanding titles. The appeal lies in cloud gaming platforms that unlock high-end experiences without upgrading local rigs, and it’s essential to weigh the cloud gaming benefits against potential cloud gaming drawbacks. Tech answers like game streaming latency, bandwidth requirements, and service libraries influence what you can play and how smoothly you can play it. To help you choose, this guide covers subscription models, platform libraries, and practical trade-offs across the major options.
Viewed through an alternative lens, this idea resembles remote game hosting, where powerful servers render the action and stream it to your device. Another way to describe it is cloud-native play or data-center powered game streaming, which emphasizes infrastructure rather than local hardware. LSI-friendly terms include cloud-based gaming, on-demand title delivery, and cross-device streaming that connects smartphones, laptops, and TVs to the same library.
Cloud gaming explained: A Deep Dive into Streaming and Accessibility
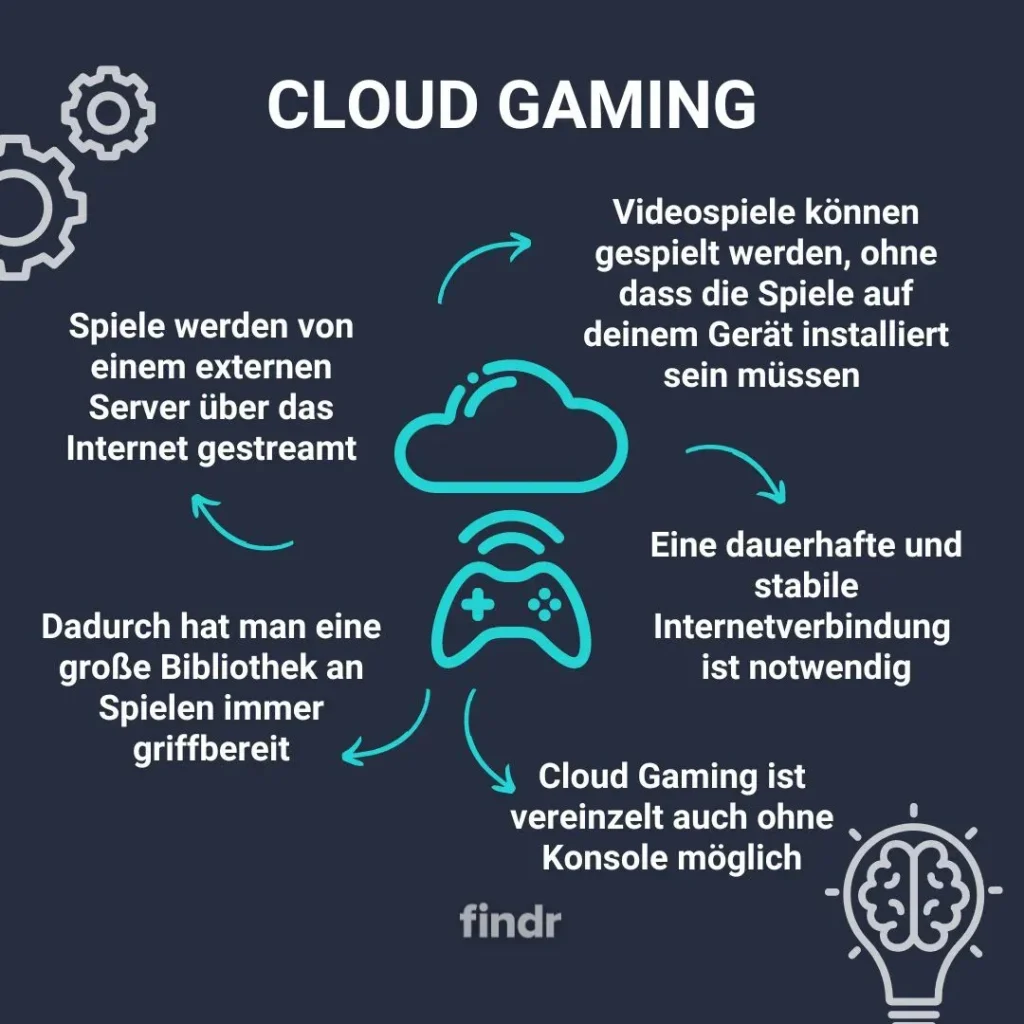
Cloud gaming explained refers to delivering games as a service by streaming from remote data centers to your device. The game runs on a powerful GPU in the cloud, while your screen shows a video stream of the action. This model is supported by cloud gaming platforms that manage encoding, delivery, and input capture. On a practical level, it means you can play demanding titles on a modest laptop, tablet, or even a smartphone with a reliable internet connection. The promise of ‘play anywhere’ is a central advantage, especially for players who do not want to invest in heavy PC builds or consoles.
However, the quality of that experience hinges on variables beyond your screen. Game streaming latency, encoding settings, and local network stability shape responsiveness and image smoothness. Providers address this with edge computing, closer data centers, adaptive bitrate, and optimized codecs, but latency and jitter can still affect fast-paced titles. Understanding these factors helps readers evaluate cloud gaming platforms and decide if the trade-offs fit their preferences. The decision often involves considering cloud gaming benefits like accessibility and reduced hardware budgets alongside potential cloud gaming drawbacks such as occasional artifacts or higher ongoing costs via subscription models.
Evaluating Cloud Gaming Platforms: Latency, Costs, and Long-Term Value
Choosing a platform means weighing latency, library breadth, and platform stability. When assessing cloud gaming platforms, close data centers and reliable networks reduce game streaming latency and improve frame pacing. Look for providers that optimize edge computing and lab test results across devices, ensuring a consistent experience on desktops, tablets, or mobile. A robust library, cross-device saves, and developer support are part of the value proposition; together they define cloud gaming benefits beyond just the price tag.
Cost considerations are often as important as performance. Most cloud gaming platforms use subscription models that grant access to a catalog of games, with tiers that unlock higher resolutions or multi-device play. Weigh the ongoing monthly cost against your expected usage, the titles you care about, and whether offline access or ownership is possible with the service. Also assess potential cloud gaming drawbacks such as data usage, throttling in certain regions, and the need for a stable connection. Understanding these trade-offs helps players maximize the return on investment while benefiting from the flexibility that cloud gaming platforms offer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does Cloud gaming explained mean in practice, and how do cloud gaming platforms address game streaming latency?
Cloud gaming explained means running games on remote data centers and streaming the video output to your device. On cloud gaming platforms, game streaming latency depends on proximity to data centers, network quality, and encoding/decoding speed. Providers optimize with edge servers, fast codecs like HEVC or AV1, and adaptive bitrate to keep inputs responsive, so you can play on modest devices with a stable internet connection.
What should I know about cloud gaming benefits, drawbacks, and subscription models when evaluating platforms?
Cloud gaming benefits include playing demanding titles without expensive hardware and enjoying flexible play across devices. Drawbacks include potential latency, occasional frame drops or compressed visuals, higher data usage, and occasional offline access limitations. Most platforms use subscription models offering libraries and tiered options; compare library size, price, and features to your preferred games and budget.
| Section | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Overview / Introduction | Cloud gaming explained moves from niche to mainstream; streams games from data centers to your device; no powerful PC required; depends on internet quality; touches on latency, quality, and costs. |
| What is Cloud Gaming Explained? | Delivery of game software as a service over the internet; game runs on remote GPU; frames streamed as video; inputs sent back; enables play on modest devices; relies on data centers, encoding, networks, and streaming protocols. |
| How It Works: The Tech Behind Cloud Gaming Explained | Game runs in cloud; server renders frames; frames encoded (H.265/HEVC, AV1) and streamed; client is a thin terminal; latency is critical; uses edge computing, adaptive bitrate, and dynamic resolution scaling; supports desktops to mobile. |
| A Look at the Landscape: Cloud Gaming Platforms | Multiple platforms with libraries, pricing, and hardware approaches; region expansion, latency improvements, features; consumer choice depends on library size, reliability, and cost; developers gain reach and monetization. |
| Benefits and Drawbacks: What Cloud Gaming Brings to the Table | Benefits: access to high-end games without upgrades; instant play; play anywhere; practical for mixed devices; developers extend lifecycle and reach; reduced local storage. Drawbacks: latency/jitter; frame drops with bandwidth changes; data usage and costs; data caps; ownership/offline concerns; may feel restrictive. |
| A Closer Look at Latency and Quality | Latency is input-to-output delay; influenced by distance, encoding, network, and routing; improvements matter for fast-action games; edge computing and codecs optimization help; choose platforms with nearby data centers and robust networks. |
| Subscription Models and Cost Considerations | Pricing often via subscriptions with tiers; library-driven or à la carte models; weigh total monthly cost against usage and preferred titles; long-term monetization considerations for publishers. |
| Who Benefits from Cloud Gaming? | Players with modest hardware and mobile gamers; households with multiple screens; indie and experimental titles more accessible; developers gain wider distribution and testing across devices. |
| Future Trends: What’s Next for Cloud Gaming Explained | Edge computing, faster networks, better codecs; 5G and ultra-wideband reducing mobile latency; more data center density and load balancing; social features, cross-platform saves, seamless device transitions; streaming becomes common option. |
| Practical Tips: Getting Started with Cloud Gaming Platforms | Ensure solid internet; wired or high-quality Wi‑Fi; 10–25 Mbps for 1080p, higher for 4K; test latency to data centers; choose input methods and display options; compare libraries and monetization. |
Summary
Table summarizes the key points about Cloud gaming explained and related topics. This should provide a quick reference to how cloud gaming works, its benefits and challenges, platforms, costs, and practical tips. The conclusion below ties these ideas together while highlighting the ongoing evolution of Cloud gaming explained.