Women’s health screenings form the cornerstone of proactive care, guiding decisions from your 20s through menopause and beyond, and they empower you to partner with clinicians to protect long-term health while building confidence in everyday wellness. A structured annual women’s health checkup sits at the center of a broader preventive strategy, coordinating basic labs, vital signs, cancer screenings, and counseling on nutrition, activity, sleep, and stress management so that follow-up feels purposeful rather than routine. As you move through life stages, the focus shifts—from cardiovascular checks and metabolic panels in young adulthood to bone health conversations and cervical cancer screening considerations in later decades—ensuring that care adapts to changing risk factors and personal goals, and invites open dialogue with your family members when appropriate. By understanding the recommended checkups, you can prepare questions in advance, interpret results with clarity, and stay on track with vaccinations, behavior changes, and targeted therapies when necessary, turning screenings into practical steps toward healthier aging. Ultimately, consistent engagement with evidence-based screenings helps reduce risk, supports early detection, and reinforces a proactive mindset so you can enjoy decades of wellness with confidence and peace of mind, knowing you have a personalized plan that respects your history, values, and life priorities.
Women’s health screenings Across Life Stages: A Guide to Preventive Care
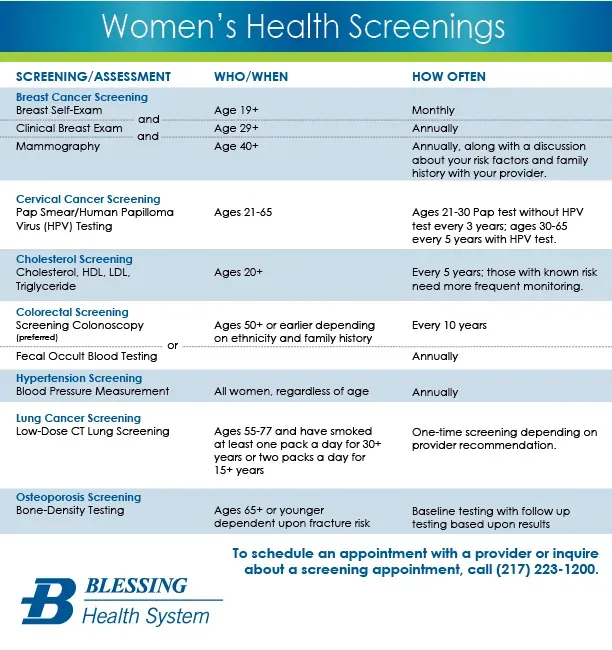
Women’s health screenings are a cornerstone of preventive care for women, guiding decisions from your 20s through menopause and beyond. When you understand which screenings matter at different life stages, you can partner with your healthcare team to protect your long-term health. This overview emphasizes why preventive care for women—and staying on top of your annual women’s health checkup—helps you detect issues early and maintain a higher quality of life across decades.
In practice, core screenings linked to age and risk include mammograms and breast health considerations, cervical cancer screening Pap test, and bone density screening for osteoporosis when indicated by risk factors. Your clinician will tailor the schedule based on age, family history, and personal risk, balancing benefits and downsides of each test. Embracing the latent semantic connections among preventive care for women, mammograms and breast health, cervical cancer screening Pap test, bone density screening for osteoporosis, and the annual women’s health checkup helps you stay informed and proactive.
Optimizing Your Annual Women’s Health Checkup with Key Screenings
An effective annual women’s health checkup is more than one appointment—it’s a coordinated plan to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol, glucose, bone health, and cancer screenings. This visit focuses on preparing for what matters most, discussing tests such as mammograms and breast health, and cervical cancer screening Pap test, and learning how to interpret results so you can act with confidence. Framing the visit within preventive care for women helps you set clear goals and stay engaged in your long-term wellbeing.
Practical steps to maximize your checkup include building a personalized screening schedule, listing medications and family history, and asking for plain-language explanations of each result. For example, you and your clinician can decide when to start or adjust mammography frequency, confirm Pap test intervals, and consider bone density screening for osteoporosis if risk factors are present. This approach keeps you connected to your health team and reinforces that preventive care for women is an ongoing process supported by your annual checkup.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the essential components of women’s health screenings during an annual women’s health checkup?
An annual women’s health checkup should include a personalized plan for women’s health screenings. Key components include cardiovascular risk assessment (blood pressure, cholesterol, glucose), discussion of bone health and, if indicated, bone density screening for osteoporosis; mammograms and breast health discussions or imaging as appropriate based on risk; cervical cancer screening with Pap test and/or HPV testing per guidelines; preventive vaccines and lifestyle counseling. Your clinician tailors these plans as part of preventive care for women, helping with early detection and long-term wellness.
How can I plan and prepare for ongoing women’s health screenings, including mammograms and cervical cancer screening Pap tests, as part of preventive care for women?
To plan and prepare, work with your clinician to build a schedule for essential screenings and wellness milestones. For mammograms and breast health, discuss starting age, frequency, and how risk factors affect timing. For cervical cancer screening Pap tests, know the recommended intervals and whether Pap with HPV testing or HPV testing alone is advised. For bone density screening for osteoporosis, determine if you have risk factors that warrant testing now or later. Keep an up-to-date health record, list medications and allergies, and bring questions about test purpose, interpretation, costs, and next steps.
| Topic | Key Points | Life Stage / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Why screenings matter | Proactive checks identify potential problems before symptoms; early detection improves outcomes; monitor risk factors (blood pressure, cholesterol, glucose, bone health); screenings support overall wellness and help you stay on track with health goals. | General preventive care |
| Ages 20s to early 30s | Baseline annual health checkup with BP, BMI, and lifestyle counseling; discuss family history, contraception, fertility planning, and mental health; cervical cancer screening (Pap/HPV) every 3–5 years; immunizations (e.g., HPV, influenza) and catch-up as needed; basic metabolic and lipid panels if indicated. | 20s–30s |
| Ages 30s to 40s | Blood pressure, lipid panel, and glucose screening become more important; mammograms decisions are guided by risk and shared decision-making; cervical cancer screening intervals adjusted to risk; consider bone health discussions if risk factors exist; continue reproductive health planning. | 30s–40s |
| Ages 40s to 50s | Cardiovascular risk assessment intensifies; mammography remains central with interval decisions; cervical cancer screening continues; bone density testing considered if risk factors or age-related risk increases; menopause-related wellness becomes a focus. | 40s–50s |
| Ages 50s and beyond | Regular cardiovascular screening; mammograms at continued intervals; colon cancer screening may begin; bone density screening commonly recommended; chronic disease risk assessment and management (e.g., diabetes, hypertension) become part of routine care. | 50s and beyond |
| Practical tips to maximize screenings | Create a personalized screening schedule with your clinician; mark reminders and due dates; prepare for appointments with medications, supplements, allergies, family history, sleep, and activity notes; understand what tests screen and how results are used; discuss risk factors; ask questions and advocate for your health; incorporate healthy lifestyle habits to support screening outcomes. | |
| How to prepare for and interpret key results | Mammograms/breast health: abnormal results may require additional imaging or biopsy; cervical cancer screening: normal results are reassuring but continue future intervals; bone density: low score prompts lifestyle changes or treatment; cardiovascular/metabolic screens: elevated BP, cholesterol, or glucose may trigger lifestyle changes or medications as guided by your clinician. | 40s–50s+ |
| Common myths and barriers to screening debunked | Screening is not just for older adults; many conditions are asymptomatic early on. Don’t assume screenings are unnecessary if you feel fine. Most preventive screenings are covered by insurance when guideline-based. Tests are usually quick and private; voice concerns with your clinician. | Myths & barriers |
Summary
Conclusion: Women’s health screenings are a cornerstone of preventive care that empower individuals to take charge of their long-term well-being. By staying on top of key screenings such as mammograms and breast health checks, cervical cancer screening, bone density checks, and comprehensive annual health reviews, you can maintain wellness milestones across life stages. Use this information to build a proactive plan with your healthcare team, adopt healthier lifestyle choices, and stay engaged in your health journey for lasting benefits.