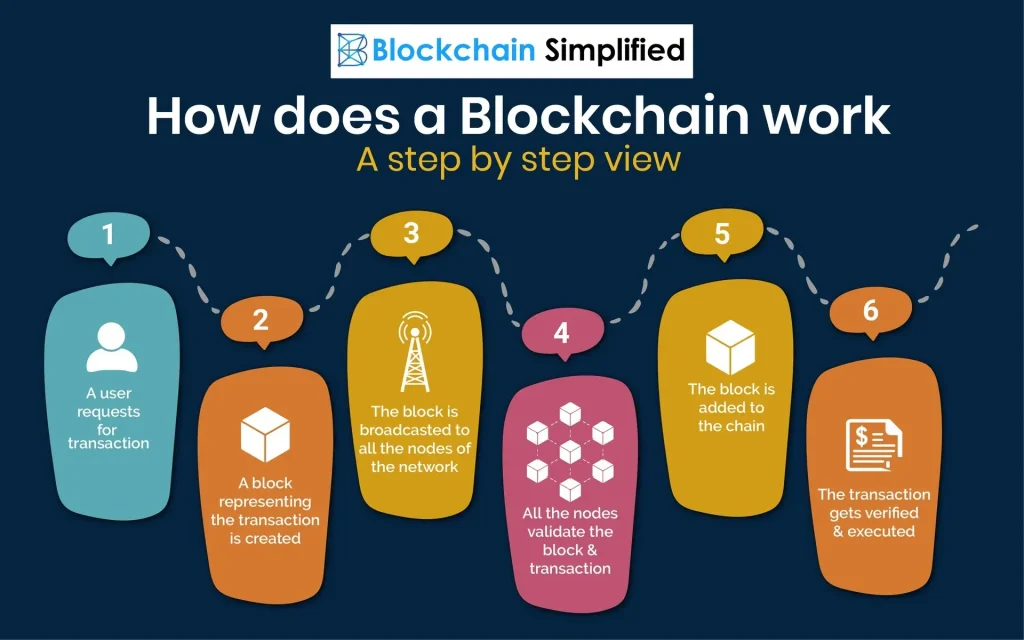
Blockchain technology, at its core, reshapes how trust is established, value is moved, and information is shared across networks. To understand its impact, many readers look to how blockchain works, the mechanism that turns transactions into tamper-evident records. The technology relies on a distributed ledger, cryptographic hashes, and consensus rules to deliver blockchain security and verifiability. Its potential spans industries, offering blockchain applications that increase transparency, improve provenance, and streamline operations. Yet organizations must weigh blockchain scalability considerations and practical benefits to decide how best to deploy it.
In practical terms, this distributed ledger approach operates as a decentralized database replicated across many machines. Instead of a central administrator, participants reach consensus to validate entries, creating an auditable trail that is resistant to tampering. Think of it as a peer-to-peer cryptographic ledger where programmable rules—smart contracts—automate agreements and reduce reliance on intermediaries. As organizations explore use cases, they weigh architecture choices such as public, private, or hybrid models to balance openness, privacy, and control.
Blockchain Technology Demystified: How Blockchain Works and Its Core Benefits
Blockchain technology sits at the intersection of cryptography, distributed systems, and trust. By distributing a ledger across many computers, it makes data tamper-evident and verifiable. The way how blockchain works—blocks of transactions, a chain of hashes, and a consensus mechanism—creates an auditable history that reduces reliance on central intermediaries. This explains why blockchain technology matters beyond the hype and highlights the core blockchain benefits, including immutability, transparency, and efficiency.
Real-world blockchain applications span finance, supply chains, healthcare, and government. By leveraging smart contracts, organizations can automate routines, improve reconciliation, and speed up settlement, all of which illustrate how blockchain works in practice and translate into tangible blockchain benefits. The combination of decentralization and governance rules ensures the ledger remains secure and auditable, enabling more interoperable networks and robust data integrity in various sectors.
From a security perspective, the cryptographic foundations underpin the entire system. Public-key cryptography and digital signatures provide non-repudiation, while consensus mechanisms defend against double-spending. These security properties, along with transparent audit trails, make the case for blockchain security as a cornerstone of trustworthy digital ecosystems and contribute to the broader value proposition of blockchain technology.
Security and Scalability in Practice: Blockchain Security, Scalability, and Real-World Applications
Businesses must balance openness with privacy and performance. Blockchain security remains strong when private keys are protected and code is rigorously audited, but vulnerabilities in smart contracts or governance gaps can introduce risk. The design choice between public, private, or consortium blockchains affects both security posture and access control, shaping deployment decisions and underscoring why good governance matters for blockchain security and reliability.
Scalability challenges are central as networks grow. Layer 2 solutions, rollups, and sharding aim to increase throughput while preserving the integrity of the main chain, addressing blockchain scalability in practical terms. Interoperability efforts help different blockchains work together, expanding blockchain applications and enabling more efficient cross-system workflows across finance, logistics, and healthcare. Ultimately, successful adoption hinges on a clear business case and governance who align blockchain strategies with real-world processes, delivering the blockchain benefits at scale while maintaining privacy and compliance.
In summary, the path to widespread use involves thoughtful architecture, ongoing auditing, and an emphasis on measurable outcomes. By focusing on blockchain security, scalability, and applications, organizations can unlock reliable, transparent, and efficient operations that extend beyond pilot projects into production-ready solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does blockchain technology work and what blockchain security features keep data safe?
Put simply, how blockchain works is a distributed ledger shared across many computers. Transactions are grouped into blocks, linked by cryptographic hashes, and added after the network reaches consensus (for example, proof-of-work or proof-of-stake). This setup, along with public-private key cryptography and digital signatures, makes records tamper-evident and secure, reducing the need for trusted intermediaries.
What are common blockchain applications across industries, and how do they demonstrate blockchain benefits like transparency and efficiency?
Blockchain applications span finance, manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and beyond. These blockchain applications highlight blockchain benefits such as transparency, traceability, and efficiency—enabling faster payments, verifiable provenance, and automated processes with smart contracts. When considering scalability, organizations often explore Layer 2 solutions and sharding to improve throughput while preserving security and interoperability.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| What it is | Blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions securely, transparently, and verifiably across many computers. |
| How it works | Transactions are grouped into blocks linked by cryptographic hashes; consensus ensures the ledger state is agreed upon; blocks form an immutable history. |
| Core technology | Nodes, consensus mechanisms (proof of work, proof of stake), cryptography (hashes, public/private keys), and digital signatures. |
| Benefits | Immutability, transparency, auditability, reduced intermediaries, efficiency; smart contracts automate actions. |
| Applications across industries | Finance, supply chains, healthcare, government, energy, governance, and data interoperability. |
| Security & privacy | Cryptographic protection; private keys must be safeguarded; privacy trade-offs exist; private/permissioned blockchains and privacy tech are options. |
| Scalability | Challenges exist; Layer 2, rollups, sharding, and cross-chain interoperability aim to improve throughput. |
| Adoption considerations | Define the problem, align with business goals, integrate with existing systems, ensure regulatory compliance, choose governance models. |
| Future outlook | Continued maturation, broader interoperability, privacy enhancements, and scalable production deployments with governance improvements. |
Summary
Blockchain technology is a transformative framework for building trusted, efficient, and interoperable digital systems across industries. By examining how it works, its benefits, and real-world applications, organizations can assess opportunities to improve security, transparency, and speed. While scalability, privacy, and governance pose challenges, ongoing innovation and pragmatic adoption are expanding the practical impact of blockchain technology. A standards-driven, thoughtful approach will help maximize value while mitigating risks.