Catastrophe bonds, often referred to as CAT bonds, are rapidly gaining recognition as a critical financial instrument in the face of escalating climate crisis effects. With increasing natural disasters on the horizon, the demand for catastrophe bond sales has surged, highlighting the necessity for innovative funding solutions. In 2025 alone, these financial instruments generated an astounding $18.2 billion in new issuance, marking an all-time record and indicating a booming market for investors and insurance companies alike. As underwriters seek to mitigate risk and ensure financial stability, ILS fund managers have become pivotal players in the ecosystem, facilitating access to vital capital during crises. By investing in catastrophe bonds, stakeholders can contribute to natural disaster funding while potentially earning attractive returns and minimizing exposure to traditional market volatility.
Also known as disaster bonds, these specialized insurance financial instruments play a crucial role in managing risks associated with severe weather events. As the climate continues to change, leading to unpredictable and destructive environmental phenomena, the market for these bonds is expanding rapidly. This growth reflects a move towards innovative funding methods that not only serve investors but also provide essential financial support for recovery efforts following calamities. The prominence of CAT bonds emphasizes a proactive approach to mitigating loss and enhancing resilience against natural disasters. Engaging with this burgeoning market enables both financial professionals and individuals to strategically navigate the complexities tied to the increasing frequency of climate-related challenges.
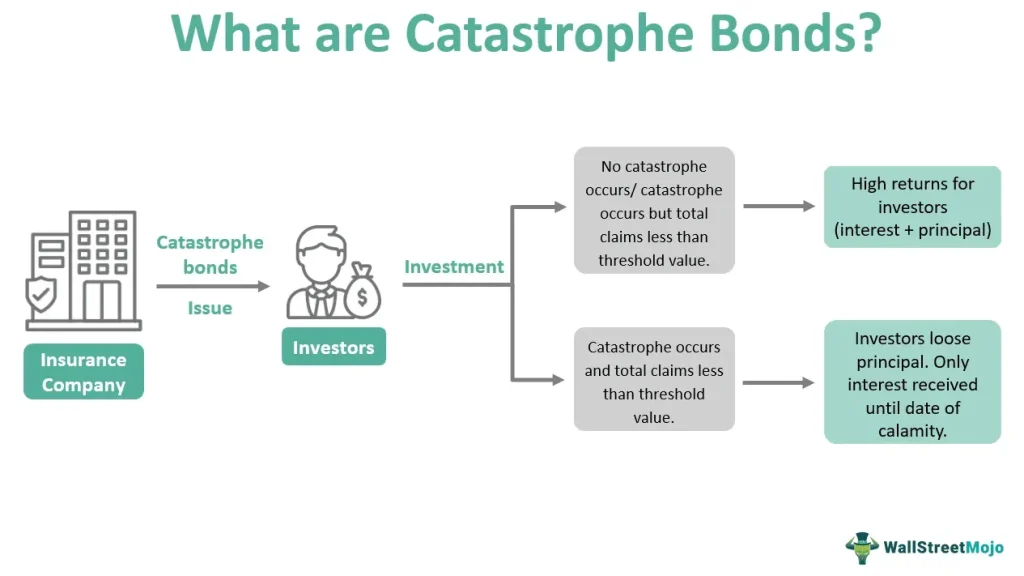
Understanding Catastrophe Bonds and Their Role in Insurance
Catastrophe bonds, often referred to as CAT bonds, are specialized financial instruments designed to provide insurers with liquidity in the wake of natural disasters. Established in the 1990s, these bonds enable insurance companies to transfer the risks associated with significant catastrophic events to investors. By issuing CAT bonds, insurers can manage their exposure to devastating losses while ensuring they have adequate cash flow to cover claims made by policyholders. The appeal of CAT bonds extends to investors who, in exchange for taking on this risk, receive attractive yields that can significantly outperform traditional debt securities.
With the increasing frequency of natural disasters driven by climate change, the importance of catastrophe bonds has surged. As severe weather events become more commonplace, insurers face mounting pressure to provide adequate protection against losses. The expansion of the CAT bond market, which reached a record $18.2 billion in 2025, highlights both the necessity of these financial instruments and the growing awareness among investors about the stability and returns associated with them. With approximately 75% of these bonds held by insurance-linked securities (ILS) fund managers, the alignment between investor interests and the pressing needs of the insurance market is becoming clearer.
The Impact of Climate Crisis on Catastrophe Bond Sales
The climate crisis is reshaping the landscape of various industries, and the insurance sector is no exception. As we experience more extreme weather events, the repercussions for insurers are profound. The sharp increase in insured losses—totaling $80 billion in the first half of 2025—demonstrates the urgent need for effective risk management solutions. Catastrophe bonds have emerged as a vital tool for insurance companies, allowing them to secure necessary funding to handle catastrophic claims. This relationship between the rising frequency of natural disasters and CAT bond sales illustrates how climate change is directly influencing the dynamics of financial market instruments.
Investments in catastrophe bonds represent a proactive approach to managing risk amid escalating climate challenges. Insurers and investors alike are becoming increasingly cognizant of the potential financial instruments available to mitigate losses associated with severe weather events. As projected, the global catastrophe bond market could exceed $20 billion in issuance in the near future. This indicates that as climate changes continue to affect natural disaster patterns, financial innovation in this sector, especially in relation to CAT bonds, will likely continue to evolve.
Investors’ Shift Towards Catastrophe Bonds and Alternative Investments
As the landscape of investment opportunities changes, investors are increasingly looking towards catastrophe bonds as viable financial instruments. CAT bonds have gained traction not only for their risk-return profile but also for their low correlation with traditional equity markets. This characteristic makes them an attractive component of a diversified portfolio, particularly as global events such as natural disasters disrupt conventional financial narratives. By allocating a portion of their portfolios to combinations of CAT bonds and other insurance-linked securities, investors can potentially benefit from resilient returns amidst market volatility.
The rise of catastrophe bond sales is also reflective of a broader shift in investor sentiment towards alternative investments amid an uncertain economic climate. Institutional investors, including pension funds and specialized ILS fund managers, see an opportunity not only to enhance the yield on their portfolios but also to contribute to societal resilience in the face of climate crises. Investing in CAT bonds means supporting the insurance industry and ensuring that resources are readily available for recovery efforts following natural disasters, creating a win-win situation for both investors and communities.
How ILS Fund Managers are Shaping the CAT Bond Market
Insurance-linked securities (ILS) fund managers play a crucial role in the disaster mitigation ecosystem by managing investments in catastrophe bonds. These professionals have the expertise to identify and invest in CAT bonds that align with their clients’ financial goals, while also addressing the pressing needs of insurers. The growth of the cat bond market, particularly the significant increase seen in recent years, has been largely facilitated by the strategic actions of these specialized managers. With 75% of CAT bonds under their management in 2025, their influence over the market dynamics cannot be overstated.
Furthermore, ILS fund managers are at the forefront of driving innovation within the catastrophe bond sector. They utilize advanced analytics and models to assess risk and enhance their investment strategies. By understanding the interaction between climate change, natural disaster trends, and insurance needs, these managers are able to construct portfolios that not only provide competitive returns but also incorporate social responsibility. Their investment decisions can further stimulate the growth of the CAT bond market as they attract more capital from investors seeking exposure to an evolving financial landscape.
The Future of Catastrophe Bonds in a Changing Climate
As climate change continues to escalate, the future of catastrophe bonds looks promising and essential. With projected losses from natural disasters increasing, the reliance on CAT bonds for managing these risks is likely to rise. The current trajectory suggests an expansion beyond conventional investors to include more diverse capital sources. This diversification can assist markets in achieving greater resilience against climate-related shocks, making CAT bonds a cornerstone in disaster risk financing.
In contemplating the future, it is crucial for stakeholders—including insurers, investors, and policymakers—to collaborate in developing frameworks that enhance the attractiveness of catastrophe bonds. As risk becomes more pronounced, the innovation of new financial products and the refinement of existing ones will underpin the evolvement of strategies aimed at funding natural disasters. More so, educational initiatives to familiarize potential investors with CAT bonds will amplify participation and drive growth in this vital sector.
Financing Natural Disasters: The Role of Catastrophe Bonds
Financing the impact of natural disasters has historically presented significant challenges for insurers and governments alike. Catastrophe bonds serve as an innovative solution to this pervasive issue, offering a mechanism for insurers to raise capital efficiently in times of crisis. By utilizing these financial instruments, insurers can ensure they have sufficient liquidity to pay out claims promptly, mitigating the financial burdens on affected communities. As natural disasters become more frequent and costly, the role of CAT bonds in funding recovery efforts will be even more critical.
The structure of catastrophe bonds allows for the transfer of risk to investors, who are willing to take on potential losses in exchange for higher yields. This symbiotic relationship not only provides insurers with the capital they need but also offers investors an opportunity to earn returns that are otherwise hard to achieve in traditional markets. As the insurance industry adapts to increasing climate-related risks and the demand for effective disaster funding grows, the integration of CAT bonds into broader risk management strategies will remain paramount.
Evaluating the Benefits of Catastrophe Bonds for Investors
For investors, catastrophe bonds present a unique opportunity characterized by appealing returns and low correlation to traditional asset classes. This allows investors to diversify their portfolios while contributing to risk management in the insurance industry. Unlike traditional investments, CAT bonds are designed to deliver returns that can be more stable, particularly during times of economic turbulence. Moreover, with the increasing frequency of climate-related events, these bonds also provide investors with a chance to engage in more socially responsible investing by directly contributing to societal resilience against disasters.
Additionally, the current climate of rising interest rates and recession fears has led investors to seek alternative asset classes that can offer favorable risk-adjusted returns. The performance of catastrophe bonds under various economic conditions has shown potential for superior risk management and yield during downturns, making them an attractive addition to the investment landscape. As investors increasingly turn to instruments like CAT bonds, it is expected that this will further stimulate market growth and innovation.
Navigating the Risks Associated with Catastrophe Bonds
While catastrophe bonds offer unique investment opportunities, they also come with inherent risks that investors must navigate. The primary risk involves the potential for loss triggered by specified catastrophic events. In the unfortunate event that a natural disaster occurs, the bond may not pay back the principal, presenting a significant loss to the investor. Therefore, it is imperative for investors to conduct thorough research and understand the specific risks associated with each CAT bond prior to investing.
Moreover, market volatility and fluctuations in interest rates can affect the attractiveness of catastrophe bonds. As the market for CAT bonds continues to evolve, investors must remain vigilant and adaptable to changing conditions. Engaging with ILS fund managers who specialize in these types of financial instruments can provide valuable insights, ensuring that investors are better equipped to manage the associated risks effectively.
The Interconnectedness of the CAT Bond Market and Climate Trends
The performance of catastrophe bonds is closely linked to climate trends and the frequency of natural disasters. As the effects of the climate crisis become more pronounced, it is essential for stakeholders in the CAT bond market to stay attuned to environmental developments. This interconnectedness emphasizes the necessity for ongoing research and modeling to better understand how climate patterns influence the demand for these financial instruments. Investors who remain proactive in monitoring these trends can capitalize on emerging opportunities aligned with the dynamics of climate change.
Additionally, predicting risk models and understanding broader market implications will provide both investors and insurers with insights needed to navigate the intricacies of catastrophe bonds. The role of innovative technology and data analytics will become increasingly important in developing sophisticated strategies, enabling market participants to respond effectively to fluctuations in climate-related risks. By leveraging such insights, the CAT bond market can thrive in an environment where climate change remains a top concern for individuals and industries alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are catastrophe bonds and how do they function as insurance financial instruments?
Catastrophe bonds, also known as CAT bonds, are specialized insurance financial instruments that raise capital for insurers facing natural disasters. When a specified disaster occurs, investors forfeit part or all of their principal to cover insurance claims, providing insurers with immediate funds to manage risks.
How do catastrophe bond sales relate to the effects of the climate crisis?
Catastrophe bond sales have surged due to the climate crisis, which has led to more frequent and severe weather events. This increase in natural disasters heightens the demand for CAT bonds, as insurers seek efficient funding solutions to handle rising claims costs.
What is the current trend in catastrophe bond sales and issuance?
Catastrophe bond sales are experiencing unprecedented growth, with issuance reaching $18.2 billion in 2025, surpassing the previous year’s record. This trend indicates a strong market response to the increasing risks posed by climate change.
Why are investors attracted to catastrophe bonds despite their connection to natural disaster funding?
Investors are attracted to catastrophe bonds because they offer the potential for equity-like returns without the volatility associated with traditional markets. Furthermore, they provide a unique opportunity to invest in financial instruments linked to natural disaster funding while contributing to risk management in the insurance sector.
What role do ILS fund managers play in the catastrophe bond market?
ILS fund managers play a crucial role in the catastrophe bond market, as they hold approximately 75% of these financial instruments. These managers, often associated with pension funds, strategically invest in CAT bonds, driving demand and facilitating growth in the market.
How significant was the financial impact of natural disasters in 2025, and what does this mean for catastrophe bonds?
In 2025, natural disasters resulted in $80 billion in insured losses and $131 billion in overall losses globally. This financial impact emphasizes the urgent demand for catastrophe bonds, as insurers require effective funding strategies to respond to unprecedented disaster-related claims.
How did catastrophe bonds evolve since their inception in the 1990s?
Since their introduction in the 1990s, catastrophe bonds have evolved significantly, becoming essential tools for risk management in the insurance industry. They have gained popularity as a mechanism for insurers to access rapid funding during crises, particularly as climate change increases the frequency and severity of natural catastrophes.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Current Sales | Catastrophe bond sales have reached $18.2 billion in 2025, breaking the previous record of $17.7 billion set in 2024. |
| Market Growth | The market for CAT bonds has expanded by 75% since the end of 2020, reaching nearly $56 billion. |
| Investor Appeal | CAT bonds attract investors due to their equity-like returns and lower volatility compared to traditional markets. |
| Natural Disaster Impact | Natural disasters caused $80 billion in insured losses in the first half of 2025. |
| Insurance Sector Innovation | Demand for CAT bonds reflects risks of climate change and the insurance sector’s financial innovation potential. |
Summary
Catastrophe bonds are becoming increasingly significant in the insurance sector, reflecting the urgent need for solutions amid rising climate-related natural disasters. The unprecedented surge in CAT bond sales to $18.2 billion in 2025 highlights not just a growing financial instrument but also a response to escalating insured losses. As the market evolves, these bonds offer critical risk management for insurers while attracting a diverse range of investors looking for stable returns in turbulent times. The continuing trend underscores the dual impacts of climate change and the innovative measures being adopted to safeguard financial interests.